Robotic Arms Manufacturer
Robotic Arms sensor solutions
- Reacting quickly
- Technical support
- After-sales support

Sensors for Industrial Robotic Arms: Enhancing Precision and Efficiency
Welcome to our page dedicated to sensors for industrial robotic arms. In today’s rapidly advancing industrial landscape, the integration of sensors plays a vital role in enhancing the precision, efficiency, and safety of robotic arm operations. This page aims to explore the various types of sensors commonly used in industrial robotic arms and highlight their benefits in improving performance and enabling automation.
Why Sensors are Essential for Industrial Robotic Arms:
- Enhanced Precision: Sensors provide real-time feedback to robotic arms, allowing them to perform tasks with exceptional accuracy. By constantly monitoring variables like position, force, and orientation, these sensors enable precise control and manipulation of objects during assembly, welding, painting, or material handling processes.
- Increased Efficiency: Sensors optimize workflow and reduce cycle times by providing crucial information for adaptive control and path planning. They enable robots to make autonomous decisions, adjust their trajectories, and avoid collisions, thereby streamlining operations and maximizing productivity.
- Improved Safety: With the ability to detect and respond to changes in their environment, sensors contribute to a safer working environment for both humans and machines. Force/torque sensors, proximity sensors, and vision systems help prevent accidents, reduce damage, and ensure compliance with stringent safety requirements in industrial settings.
- Intelligent Decision-Making: Sensors equipped with advanced technologies, such as artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML), enable robotic arms to analyze data, adapt to changing conditions, and learn from experience. This leads to improved decision-making capabilities, optimized processes, and increased autonomy in robotics applications.
Types of Sensors Used in Industrial Robotic Arms:
- Force/Torque Sensors: These sensors measure forces and torques applied by the robot during interactions with objects. They provide feedback that enables delicate grasping, precise assembly, and collaborative operations between robots and human workers.
- Proximity Sensors: Proximity sensors detect the presence or absence of objects in the robot’s workspace. They help prevent collisions, ensure accurate positioning, and enable seamless interaction with other equipment or parts.
- Vision Systems: Vision systems utilize cameras and image processing algorithms to capture and analyze visual information. They enable robotic arms to recognize objects, track positions, perform quality inspections, and facilitate complex tasks such as bin picking and object manipulation.
- Inertial Measurement Units (IMUs): IMUs consist of accelerometers and gyroscopes that measure changes in position, orientation, and angular velocity. These sensors enhance the robot’s spatial awareness, enabling precise movements, motion planning, and stabilization.
- Temperature and Environmental Sensors: These sensors monitor temperature, humidity, air quality, and other environmental factors within the robot’s surroundings. They ensure optimal operating conditions, prevent overheating, and support predictive maintenance routines.
Benefits of Using Sensors in Industrial Robotic Arms:
- Increased Accuracy and Quality: Sensors enable precise control and feedback, resulting in higher product quality and consistency. They reduce errors, minimize rework, and improve overall process accuracy.
- Improved Efficiency and Productivity: With sensors guiding robotic arm movements, tasks can be executed more efficiently, reducing cycle times and increasing throughput. This leads to improved productivity and cost-effectiveness.
- Enhanced Flexibility and Adaptability: By integrating sensors, robotic arms can handle a wider range of tasks, adapt to different workpieces, and accommodate variations in shape, size, or material properties. This flexibility allows for seamless reconfiguration and rapid deployment across diverse applications.
- Enabled Human-Robot Collaboration: Sensors play a crucial role in facilitating safe and productive human-robot collaboration. With the ability to detect and respond to human presence, force/torque sensors ensure safe interactions and enable cobot applications.
- Future-Proofing Capabilities: As robotics continues to evolve, sensors serve as a foundation for future advancements. By integrating smart sensors and leveraging emerging technologies like AI and ML, industrial robotic arms can continually improve and adapt to changing demands.
Sensors are essential components of industrial robotic arms, revolutionizing automation in manufacturing and other industries. They enable enhanced precision, efficiency, safety, and adaptability, contributing to improved productivity and product quality. Embracing the power of sensors empowers businesses to unlock new possibilities and stay ahead in the dynamic world of industrial robotics. Contact us today to discover how our sensor solutions can optimize your robotic arm operations.
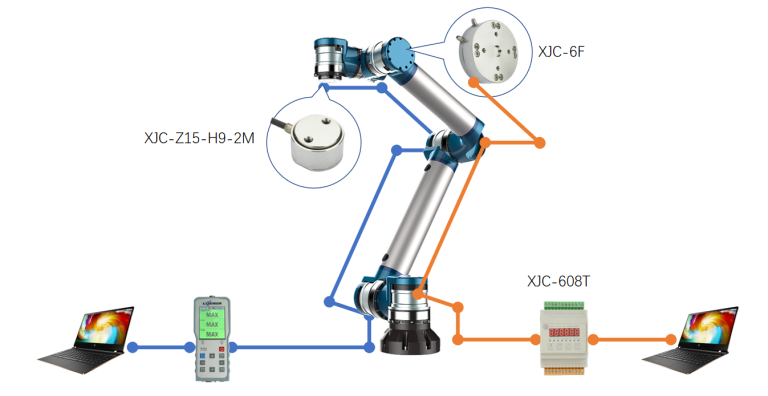
Sensors for robotic arms in our factory
Compression Load Cell X-Z15-H9-2M

Features
● XJC-Z15-H9-2M adopts high-precision resistance strain principle;
● Meet force measurement in the range of 0-20kg;
● Pressure-bearing, easy to install;
● Small size, beautiful appearance;
● High response frequency, high-precision;
Technical Parameter
| Capacity | 0-20 kg | Material | Stainless steel |
| Nonlinearity | 0.05%F.S. | Rated output | 2.0±10% mV/V |
| Recommended excitation | 5V-10VDC | Maximum excitation | 15VDC |
| Protect class | IP64 | Compensated temp range | -10~40°C |
| Hysteresis | 0.05%F.S. | Operating temp range | -20~80°C |
| Repeatability | 0.05%F.S. | Insulation | ≥5000MΩ/100VDC |
| Input impedance | 350Ω ± 10Ω | Output impedance | 350Ω ± 5Ω |
| Creep(30min) | 0.05%F.S. | Temp effect on output | 0.1%F.S./10°C |
| Zero balance | ±2%F.S. | Temp effect on zero | 0.1%F.S./10°C |
| Limit load | 150% | Breaking load | 200% |
| Cable size | Ø2x4m | Life | Full scale more than 1 million times |
| Cable Connection | Ex+: Red;Ex-: Black;Sig+: Green;Sig-: White | ||
6 Aixs force sensor X-6F

Features
● Quick response;
● High precision with the principle of resistance strain type;
● Good temperature characteristics with selfcompensated strain gauge;
● Decoupled structure, tiny long-term crosstalk error;
● Small size, low height, suitable for small-volume applications;
● Size and range can be customized;
Technical Parameter
| Non-linearity | ≤±0.5%F.S. | Repeatability | ≤±0.05%F.S. |
| Zero balance | ±5%F.S. | Operating temp range | -20~80°C |
| Compensated temp range | -10~40°C | Insulation | ≥2000MΩ/50VDC |
| Recommended excitation voltage | 5VDC | Safe load limit | 300%F.S. |
| Temp effect on output | ≤0.2%F.S./10°C | Temp effect on zero | ≤0.2%F.S./10°C |
| Long-term crosstalk error | ≤3-5%F.S. | Protection class | IP65 |
| Cable size | φ2.4*3m+Lemo14 PIN plug (Option) | ||
Digital control indicator XJC-608T

Features
● Built-in multistage amplifier chip, independent power supply for sensor.
● Multiple sensitivity input, and switchable.
● High speed, high transmission speed, and high dynamic response frequency.
● Good long-term stability, good anti-interference performance.
Application
Voltage transmitter can work together with strain gages,ceramic piezoresistive sensors, and diffusedsilicon piezoresistive sensors which can realize the conversion and transmitting of physical quantity,such as force, pressure, weight, displacement, torque and liquid level.And the signal can be directlyinput in computers or other measurement and control instruments.
Technical Parameter
| External power supply | 5VDC | Material | Plastic |
| Power supply | 12VDC 24VDC | Rated input | 0.5-3.0mV/V |
| Non-linearity | 0.1%-0.03%F.S. | Resolution | 1/50000 |
| Hysteresis | 0.1%-0.05%F.S. | Sampling speed | 15-1920Hz |
| Repeatability | 0.1%-0.05%F.S. | Operating temp range | -10℃ to 50℃, Humidity Below 85% RH |
| Zero balance | ±2%F.S. | Display accuracy | -199,999-999,999 |
| Power Consumption | about 5W | Communication Interface | RS232, RS485,0-10V,4-20mA |
| Cable connection | Ex+: Red;Ex-: Black;Sig+: Green;Sig-: White (in) | ||
Transmitter X-CF805T

Features
● Display digits: 6-digit
● Reset: panel, switch input, clear command;
● Analog transmission: 0-10V,±10V
● Digital output: RS232,RS485
● Protocol: MODBUS-RTU,TC-ASCII
● Analog transmission range: -100% – +100%FS
● Power reverse polarity protection.
Technical Parameter
| Power supply | 12V/5W | AD resolution | 24 bit |
| Sensor’s supply voltage | 5VDC,200mA | Sampling rate | 15-1920 Times/Sec. |
| Input signal range | 0-20mV | Transmitting speed | =Sampling rate |
| Non-linearity | 0.01%F.S. | Function | High-speed curve catch |
| Accuracy | 0.5%F.S. | Display | LCD |
Description
It can match with various resistance strain sensors , ceramic piezoresistive sensors and diffusion silicon piezoresistive sensors to convert and transmit physical quantities such as force, pressure, weight,displacement, torque, liquid level etc,. It matches with all kinds of sensors developed and produced by our company, and the signal can be directly input into the computer or measure and control instrument.
Frequently Asked Questions:
A: The type of sensor used in a robotic arm can vary depending on its specific application. Commonly used sensors include force/torque sensors, proximity sensors, vision systems, and inertial measurement units (IMUs).
A: Sensors in robotics serve various purposes such as providing feedback on position, force, and orientation, detecting objects or obstacles, enabling vision-based perception, ensuring safety by preventing collisions, and facilitating precise control and interaction with the environment.
A: The arm processor in robotics refers to the central processing unit (CPU) responsible for controlling the movements and operations of the robotic arm. It handles tasks such as motion planning, trajectory generation, and actuator control.
A: Factory robots may be equipped with a range of sensors depending on their intended tasks. Common sensors used in factory robots include vision systems for object identification and inspection, proximity sensors for collision avoidance, force/torque sensors for accurate force control, and encoders for precise position feedback.
A: Industrial robotic arms commonly use a variety of sensors to enhance their capabilities. These may include force/torque sensors for precise force control, proximity sensors for object detection and positioning, vision systems for visual guidance and inspection, and IMUs for measuring orientation and angular velocity.
XJCSENSOR is a leading manufacturer of sensors specifically designed for robotic applications. Our company specializes in developing high-quality, reliable, and technologically advanced sensors to meet the diverse needs of the robotics industry. With our expertise and dedication to innovation, we strive to provide cutting-edge sensor solutions that enhance the performance and capabilities of robots. Contact XJCSENSOR today to explore our range of sensors tailored for robotic systems.