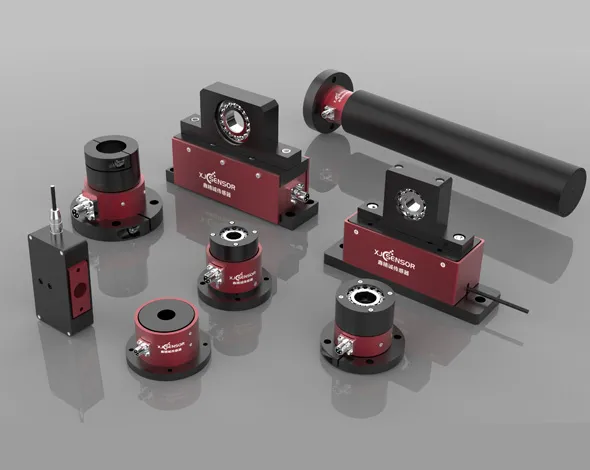
In modern manufacturing, the quest for efficiency, consistency, and safety has led to a technological evolution. It’s called industrial automation. At the heart of this transformation lies an array of sophisticated sensors that serve as the eyes and ears of automated systems. Force sensors have emerged as critical components. They facilitate refined control and monitoring. In this blog post, we delve into the types of sensors utilized within factory settings. We also highlight key industrial automation products. We unravel the remarkable applications of force sensors.
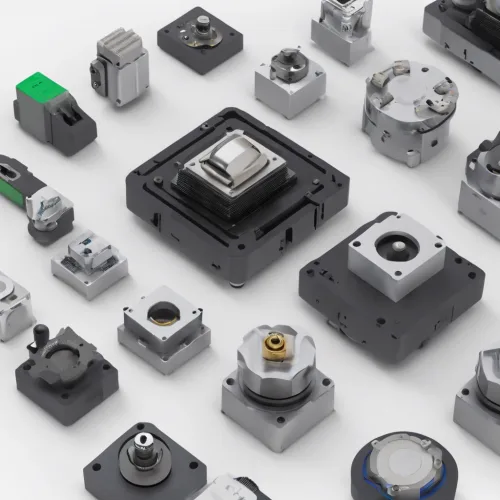

The Spectrum of Sensors in Factory Automation
Factory automation relies heavily on various types of sensors to function effectively:
Proximity Sensors
Photoelectric Sensors
Vision Systems
Temperature Sensors
Pressure Sensors
Force Sensors
Each sensor type is selected based on its suitability to perform a specific function within the automation process. Force sensors hold a special place due to their versatility and direct impact on product handling and manipulation.
Industrial Automation Products: Enhancing Operational Excellence
Industrial automation products encompass a broad range of technologies. They are designed to automate complex processes in manufacturing. Some notable examples include:
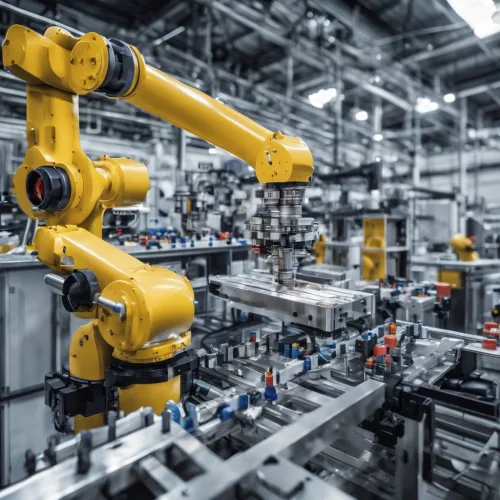

- Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs): Serve as the brains of the automation system, executing control functions based on real-time data.
- Robotic Arms: Execute repetitive tasks with high precision, often integrated with force sensors to adjust grip and handling pressure.
- Human-Machine Interfaces (HMIs): Allow operators to interact with and oversee the automated system.
- Sensors and Transducers: Including force sensors, they transform physical properties into quantifiable data that can inform automated decisions.
Force Sensors: The Touch of Precision in Automation
Force sensors are indispensable in industrial automation. They can ensure delicate yet firm manipulation of materials. They can detect and measure the amount of force being applied by robotic arms or other automated machinery. This leads to two primary benefits:
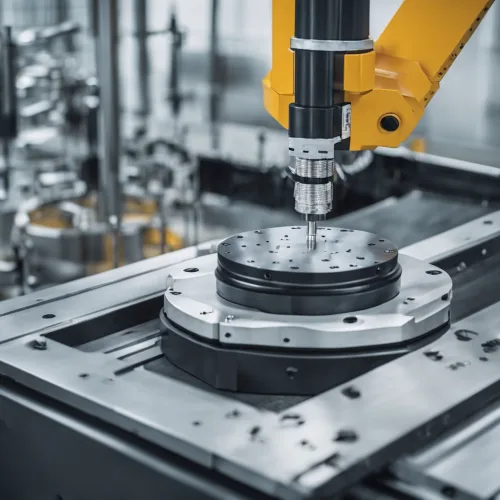

- Quality Control: By measuring the force used in assembly operations, force sensors help in maintaining consistency and detecting when parts are not assembled correctly due to variations in force.
- Equipment Protection: Overexertion of force can damage machinery. Force sensors play a defensive role by preventing excessive force application.
Industrial Automation Examples Utilizing Force Sensors
- Packaging Machinery: Ensuring proper sealing pressure in food packaging to maintain product freshness.
- Material Testing Equipment: Applying controlled force to test material durability and strength.
Applications of Force Sensors
- Precision Assembly: Enabling robots to perform tasks such as inserting, mounting, and screwing components with exact force.
- Weighing Systems: Using force sensors to dynamically weigh products during transport on conveyor systems.
- Tactile Feedback: Providing feedback to robotic systems for adaptive pressure control, enhancing their ‘sense of touch’.